To access material, start machines and answer questions login.

Nmap is a free open source tool, employed to discover hosts and
services on a computer network by sending packets and analyzing the
retrieved responses. In this task nmap will be used to enumerate open ports and what services are running on machine. Check out the Nmap room for more on this!
| Nmap Flag | Example | Description |
| -p | nmap -p 21 MACHINE_IP | Port scan for port 21 |
| -p- | nmap -p- | Port scan all ports |
| -Pn | nmap -Pn MACHINE_IP | Disable host discovery. Port scan only. |
| -A | nmap -A MACHINE_IP | Enables OS detection, version detection, script scanning, and traceroute |
| -sC | nmap -sC MACHINE_IP | Scan with default NSE scripts. Considered useful for discovery and safe |
| -sV | nmap -sV MACHINE_IP | Attempts to determine the version of the service running on port |
| -v | nmap -v[-vv] MACHINE_IP | Increase the verbosity level (use -vv or more for greater effect) |
| -oA | nmap MACHINE_IP -oA nmap_ouput | Output in the three major formats at once |
| --script | nmap --script http-sql-injection | Scan with a single script. Example checks for sql injections |
| --script-args | --script-args nmap --script snmp-sysdescr --script-args snmpcommunity=admin | NSE script with arguments |
In this task:
- First scan which ports are open on the box: nmap -p- -vv
MACHINE_IP - Then after finding the ports number, enumerate what services are running on those port:
nmap -A -p port1,port2,port3 MACHINE_IP
How many ports are open?

John the Ripper is an Open Source password security auditing and password recovery tool available for many operating systems.
Check out the Crackthehash or Crackthehash2 for more hash cracking.
To crack ssh private key first use ssh2john python script convert private key to hash (It comes with Kali Linux. Run locate ssh2john).
python path/to/ssh2john.py privatekey > privatekey.hash
Then use john to crack the hash.
john privatekey.hash -w=/path/to/wordlist
Crack the passphrase of the private key and SSH into the machine. Make sure to change the file permissions of SSH private key to 600.
What is the passphrase for the RSA private key?

According to Wikipedia SSH or Secure Shell is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Typical applications include remote command-line, login, and remote command execution, but any network service can be secured with SSH.
Some important flags that will be used in this task are below.
| Flag | Description |
| -i | If you want to access a remote server using a private key. |
-L | For local port forwarding. Followed by local_port:remote_address:remote_port |
| -R | For remote port forwarding. Followed by port:local_address:local_port |
| -D | For Dynamic port forwarding. Creates a socks proxy on localhost. Followed by local_PORT
|
| -N | Do not execute a remote command. This is useful for just forwarding ports |
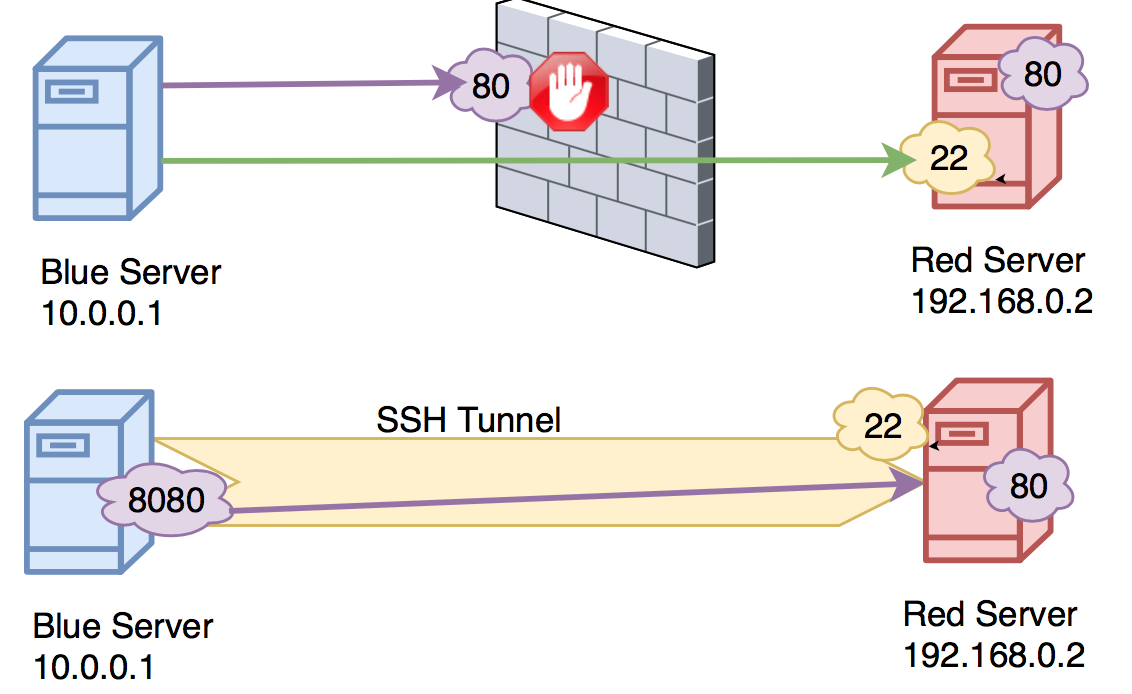
In the above picture the user from blue server wants to connect to port 80 on the red server but the port is blocked by the firewall. User can connect through ssh and create a tunnel which would allow him to connect to port 80 on the red server. In this case user can use Local port forwarding to connect the port on the red server to his local machine.
To complete this task:
- Setup Dynamic Port Forwarding using SSH.
HINT:-i id_rsa -D 1337 - Set up proxychains for the Dynamic Port Forwarding. Ensure you have commented out
socks4 127.0.0.1 9050in your proxychains configuration and addsocks5 127.0.0.1 1337to the end of configuration file (/etc/proxychains.conf).
The file name may vary depending on the distro you are using.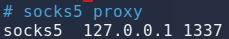
- Run a port scan to enumerate internal ports on the server using proxychains. If you use Nmap your command should look like this
proxychains nmap -sT 127.0.0.1. - After finding the port of the webserver, perform Local Port Forwarding to that port using SSH with the -L flag.
HINT:-i id_rsa -L 80:127.0.0.1:(remote port)(Try using with sudo)
Use nmap to scan for the vulnerability in the CMS that is running on the webserver. Nmap has a script that can find vulnerabilities in the CMS which used in this machine.
Now that you have locally forwarded the port, the webserver is running on localhost and you can access it from your browser.
In this task:
- Scan the internal web server and find vulnerable plugins using Nmap or the popular scanning tool for this CMS.
- Exploit the vulnerability either using metasploit or following any POC(proof of concept).
- Get the user flag.
What CMS is running on the machine?
Can you find any vulnerable plugins?
What is the CVE number for directory traversal vulnerability?
There is a metasploit module for the exploit. You can use it to get the reverse shell. If you are feeling lucky you can follow any POC( Proof of Concept).
What is the user flag?

- Find that user has left password somewhere accidentally. Management now requires SSH sessions to be logged.
- Guess the user's new password.
- Get the root flag.
________________________
< Made with ❤ by BadByte >
------------------------
\ ^__^
\ (oo)\_______
(__)\ )\/\
||----w |
|| ||
What is the user's old password?
What is the root flag?
Ready to learn Cyber Security? Create your free account today!
TryHackMe provides free online cyber security training to secure jobs & upskill through a fun, interactive learning environment.
Already have an account? Log in