
To access material, start machines and answer questions login.
Task 1Introduction
Imagine you have a fantastic idea for an app that helps students practice cyber security, and you host it on your own computer in your country. But what can you do when users from other parts of the world try to access it and experience lag? What if many students connect at the same time, or your computer is turned off? These limits make it hard for the app to grow.
That's when cloud computing comes to play and solves these problems!
The cloud is built on top of technologies you already learned, like virtualization and containers. These enable running many applications efficiently on shared infrastructure and quickly creating or changing environments when needed.
In this room, we will explore the basics of cloud computing and how this impacts the way modern applications are built, deployed, and used every day.
Learning Objectives
- What is cloud computing
- Service models of cloud (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
- Cloud Types (Private/Public/Hybrid)
- Benefits of cloud computing
- How big companies are using the cloud
Prerequisites
Answer the questions below
Let's go!
Task 2Cloud Computing Overview
Cloud computing is the perfect solution for the challenges in the application you’ve designed, such as moving your files from a single laptop to online storage that you can access anywhere. Instead of running your app on one computer in one country, the cloud lets you use computing resources over the internet. This makes your application easier to access, more reliable, and ready to grow as more students start using it.
How Servers Evolved to Cloud
Before we start diving into cloud details, it’s helpful to understand that cloud computing did not appear suddenly. It is the result of many years of changes in how servers were used and managed. At each step, businesses looked for ways to reduce costs, use resources more efficiently, and make their applications easier to run and scale. The timeline below shows this evolution, from physical servers to the cloud we use today:

Cloud Benefits and Characteristics
After seeing how applications evolved from physical servers to the cloud, it's becoming clear why cloud computing is so widely used today. The cloud was designed to address common problems, including limited capacity, high costs, and slow growth.
The following benefits and characteristics explain how cloud computing makes applications easier to run, scale, and manage:
- Scalability: Easily scale up or down as your application's needs change.
- On-demand self-service: Create or remove servers and storage instantly, without waiting for hardware.
- Pay only for what you use: You are charged based on usage, not upfront costs.
- Security: Cloud providers protect the infrastructure with strong security measures.
- High availability: Applications keep running even if part of the system fails.
- Global access: Your application can be accessed by users anywhere in the world.
In simple terms, the cloud enables IT resources to be flexible, cost-effective, and easier to manage.
Types of Cloud
The flexibility provided by cloud computing allows applications to be run in different ways, depending on your needs and level of control. Because of this, cloud providers offer multiple models for deploying and using applications, each suited to different scenarios.
Let’s start with the deployment types you can choose for a cloud environment:
- Public Cloud: Used by startups, websites, and global apps because it is affordable, easy to scale, and requires no infrastructure management. Public cloud services are preferable for nearly every use case.
- Private Cloud: Used by banks, healthcare, and government organizations because it offers greater control, customization, and compliance for sensitive data.
- Hybrid Cloud: Used by companies like e-commerce platforms that need to keep sensitive data private while still scaling publicly during high demand.
Just like there are different ways to deploy a cloud environment, there are also different ways to use cloud services. Depending on your experience and needs, you can choose the level of responsibility that fits your application.
Let’s look at the main cloud service models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): You rent basic computing resources such as virtual servers, storage, and networking. You are responsible for managing the operating system and your application, while the provider manages the physical hardware.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): The cloud provider manages the infrastructure and the operating system. You focus on building, deploying, and running your application without worrying about servers.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): You use a complete application over the internet. The provider manages everything, and you access the software through a browser or app, for example, Gmail or Zoom.
Think of cloud service models like different ways of renting a place to live:

Major Cloud Vendors
There are several cloud vendors offering a variety of services, but Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the industry leader, with the most extensive offerings and global reach. Other well-known cloud providers include:
- Microsoft Azure: A strong competitor, especially in enterprise and hybrid cloud environments.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Known for powerful data analytics, AI, and machine learning tools.
- Alibaba Cloud: A major player in Asia, offering competitive cloud services globally.
- IBM Cloud: Focuses on hybrid cloud and AI-driven solutions for businesses.
- Oracle Cloud: Focuses on enterprise applications and databases.
Each of these vendors offers a range of services, but AWS remains the most popular due to its vast infrastructure and support for businesses of all sizes.
How Companies Are Using the Cloud
- Netflix runs its entire platform on AWS so it can scale globally, stay online during peak demand, and stream content reliably to millions of users at once.
- Spotify uses the cloud to handle millions of songs and users, scaling quickly when new music or features are released.
- Instagram relies on the cloud to store massive amounts of photos and videos and deliver them fast to users around the world.
- Online stores use the cloud to handle traffic spikes during black friday without buying permanent infrastructure.
These companies use the cloud because it lets them scale easily, reduce costs, stay reliable, and focus on improving their products instead of managing hardware.
Next, you’ll apply these same ideas by deploying your cyber security training app in a simulated cloud environment!
Answer the questions below
What is the characteristic of cloud environments that enables you to handle an unexpected increase in access to your application?
What is the most common type of cloud deployment used?
Suppose you want to deploy an application to the internet, focusing only on application development and leaving infrastructure to others. What type of cloud service is the best?
Task 3Deploying a Cloud Instance
Task includes website
So far, you’ve learned what cloud computing is and why companies use it. Now it’s time to see those ideas in action by deploying a cloud environment to launch your cyber security app training!
In this exercise, you’ll use a cloud interface similar to the AWS platform. The goal is not to memorize buttons, but to understand how cloud resources are easily created and managed in a real-world scenario.
Open the Cloud Console site by clicking the View Site button below, and let's create your cloud environment!
Basic Cloud Terminology
To complete this exercise, you only need to understand a few basic concepts from AWS:
- EC2 (Virtual Computer / Server): EC2 represents a virtual computer in the cloud. Just like a real computer, it has a CPU and memory (RAM) and can run applications. Whenever you add an EC2 instance, you are adding a computer to your environment.
- Instance Type (for example: t2, t3, m5): Instance types describe how powerful the virtual computer is. Some have more CPU and RAM and are therefore more expensive. You choose the Instance Type based on your needs, knowing that:
- Bigger instances = more power + higher cost
- Minor instances = less power + lower cost
Deploying Your Environment
You will create three virtual computers (EC2 instances) to host your cyber security training application. This aligns with the Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) model you previously learned, as cyber security practices often require full access to the operating system. This allows you to install tools, configure the system, and safely simulate attacks and defenses, just like in real-world environments!
Picking a Region
First, you need to choose a region where your resources will live. You can do it in the top right of your screen:
A region represents a geographical location, for example, Europe or North America.
Creating Virtual Machines
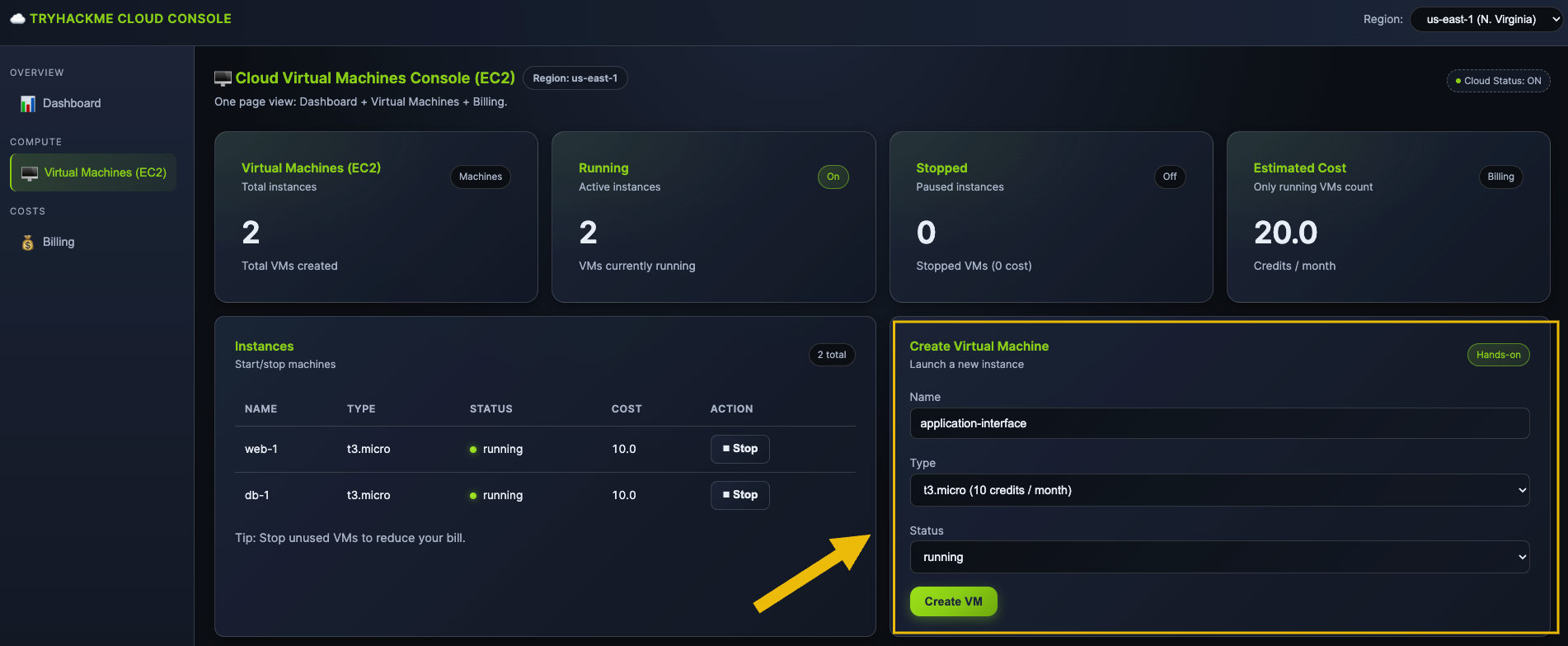
Now, go to the Create Virtual Machine block on the right side of the page to create the virtual machines for your application.
First, let's create your application interface machine. Set the following configuration:
- Instance Name:
application-interface - Instance Type:
t3.micro - Status:
running
Now, let's create two testing computers for users to practice their cyber security skills.
Since these are test machines, let's use a more powerful instance type: m5.large.
Machine 1:
- Instance Name:
study-machine-1 - Instance Type:
m5.large - Status:
running
Machine 2:
- Instance Name:
study-machine-2 - Instance Type:
m5.large - Status:
running
After creating the two new machines, your Instances block should look like this:
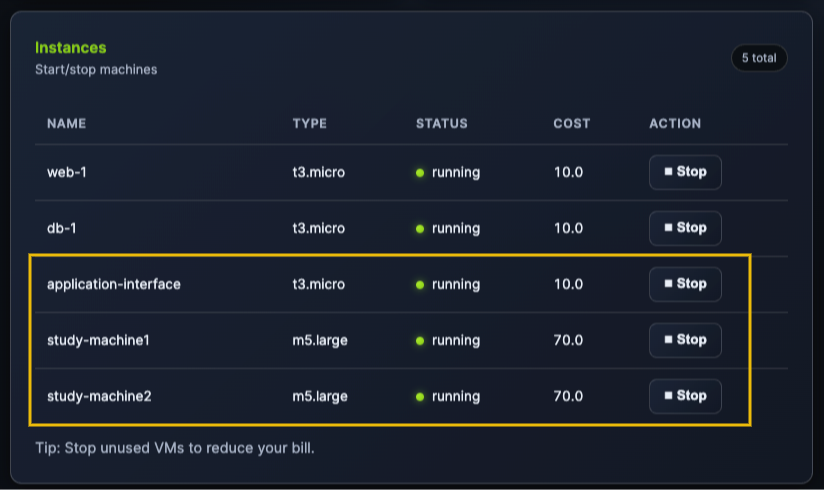
Billing Analysis
Let's analyze how much credit is costing our environment by navigating to the Billing section at the bottom of the page.
There, you can check how much each type of instance is costing you, as well as the total.
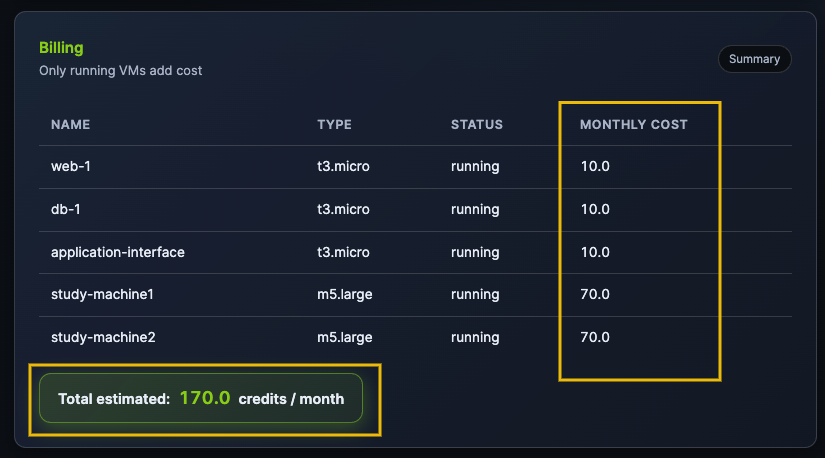
Currently, you are still developing your application, so users have not yet accessed your platform. We can optimize costs by stopping the two study machines and reviewing the new cost of your environment.
Go to the Instances block and click the Stop button for both study-machine-1 and study-machine-2.
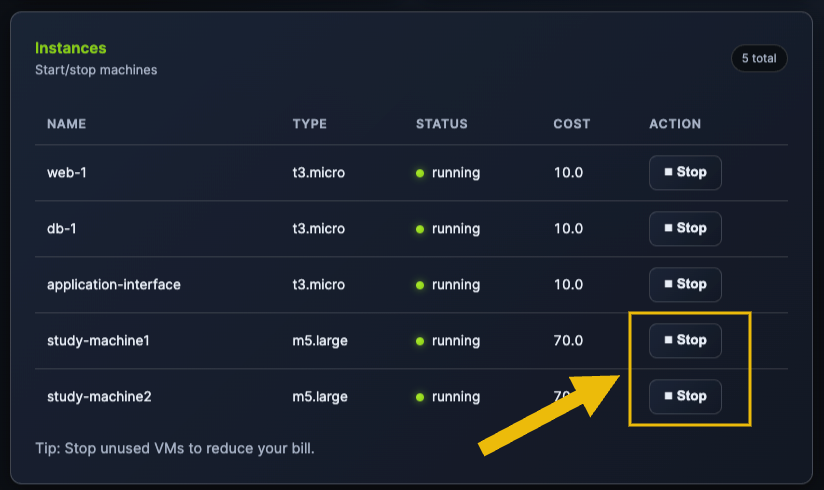
Go back to the Billing section, and you should see that your cost was reduced considerably:
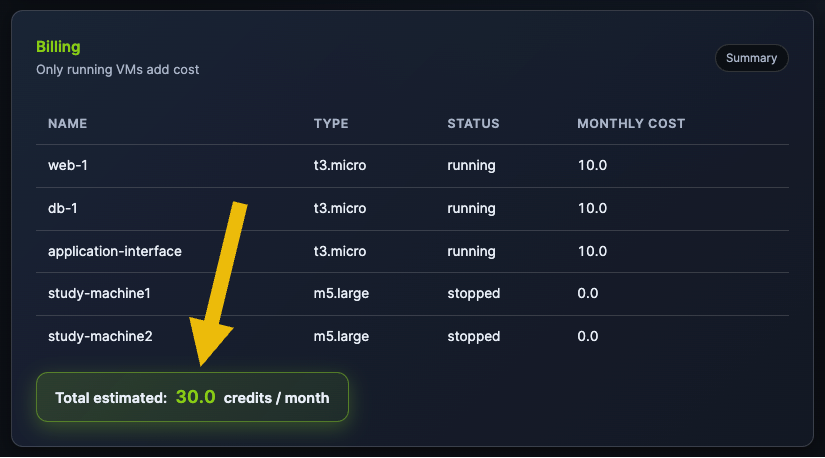
This exercise is a clear example of how easily you can change and manage your costs in a cloud environment.
Answer the following questions to conclude your learning about cloud computing!
Answer the questions below
What is the total cost of credits of the entire environment if study-machine-1 and study-machine-2 are stopped?
How many credits does an m5.large EC2 instance cost per month?
What is the total cost of credits if only the new instances we created are running?
What would be the total running cost of the entire environment you created if you add a third t3a.small study machine?
Task 4Conclusion
In this room, you explored the core ideas behind cloud computing and how it enables flexible, scalable, and cost-effective access to computing resources.
Key Terminology
Let's quickly review some concepts we learned in this room:
- Public Cloud
Cloud services you access over the internet that many people and companies share. - Private Cloud
A cloud built just for one company, so they have more control and security. - Hybrid Cloud
A mix of public and private clouds that can work together and share data. - IaaS
A service where you rent basic computer parts like servers and storage from the cloud. - PaaS
A service that gives you a ready-to-use environment to build and run apps without managing servers. - SaaS
Software you use online without installing anything, like Gmail or Zoom. - EC2
Amazon’s cloud computers that you can quickly create, use, and resize whenever you need them.
We also concluded that the key benefits of cloud computing are:
- Scalability
- On-demand self-service
- Pay only for what you use
- Security
- High availability
- Global access
Further Learning
You are now ready to explore the next key area: Operating Systems. In the Operating Systems Introduction room, you will learn how OS components manage hardware, processes, memory, and security. This knowledge is essential for understanding how cloud systems run applications behind the scenes!
Answer the questions below
I'm ready for the next module!
Ready to learn Cyber Security? Create your free account today!
TryHackMe provides free online cyber security training to secure jobs & upskill through a fun, interactive learning environment.
Already have an account? Log in
